Sadly, Visual Studio 2010 does not include any F# web application project type.
In practice, this means that if you want to use F# in a web project (be it MVC or WebForms), you have to start with a basic "F# library" project, then manually create a web.config or copy it from somewhere else, manually create a global.asax, global.asax.fs, etc. Or you can let the main web project (i.e. the one with the Global.asax) be a normal C# web app project and reference a F# library where the controllers/webforms are defined.
Another minor annoyance is that you lose the F5 functionality to launch the application, since Visual Studio doesn't know it's a web application. A couple of workarounds for this:
- Reference the VS built-in dev web server as the starting external program. This is usually in
C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\microsoft shared\DevServer\10.0\WebDev.WebServer40.EXEThe downside of this is that it doesn't automatically launch your default web browser to your app. It might sound somewhat silly, but when you're used to getting a browser immediately, automatically, it's kind of annoying not having it.
- Write a little wrapper around WebServer40.exe that launches a browser. Here's the code:
open System open System.IO open System.Diagnostics open System.Reflection [<EntryPoint>] let main args = // code adapted from FSharp.PowerPack's AspNetTester let progfile = let prg = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.ProgramFiles) if Environment.Is64BitProcess then prg + " (x86)" else prg let webserver = Path.Combine(progfile, @"Common Files\microsoft shared\DevServer\10.0\WebDev.WebServer40.EXE") if not (File.Exists webserver) then failwith "No ASP.NET dev web server found." let getArg arg = args |> Seq.tryFind (fun a -> a.ToUpperInvariant().StartsWith arg) let webSitePath = match getArg "PATH:" with | None -> Directory.GetParent(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()).FullName | Some a -> a.Substring 5 let port = match getArg "PORT:" with | None -> Random().Next(10000, 65535) | Some a -> Convert.ToInt32 (a.Substring 5) let vpath = match getArg "VPATH:" with | None -> "" | Some a -> a.Substring 6 let pathArg = sprintf "/path:%s" webSitePath let portArg = sprintf "/port:%d" port let asm = Assembly.LoadFile webserver let run (args: string[]) = asm.EntryPoint.Invoke(null, [| args |]) :?> int Process.Start (sprintf "http://localhost:%d%s" port vpath) |> ignore run [| pathArg; portArg |]
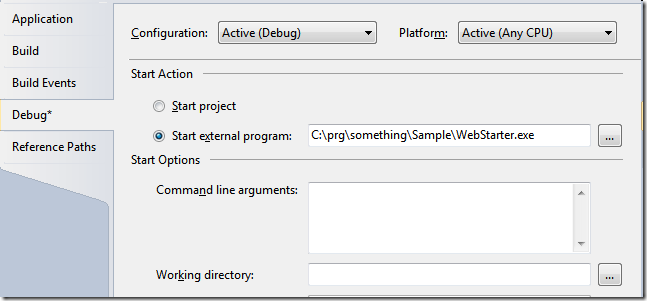
Place the exe (I called it WebStarter.exe) in your web app root, then put it as starting external program:You can optionally define a fixed port (by default a random port is used), a different root path or a virtual path to start the browser. Set your F# web app project as "Startup Project", hit F5 and voilà, browser launches with the debugger hooked up :)
- UPDATE: Steve Gilham has another solution, you can just add a couple of elements to the fsproj to turn it into a web app project.
- UPDATE: Tomas Petricek created a MVC project template.